使用文件存储数据 | 臭大佬
简介
在日常工作和学习中,我们经常使用文件来存储数据,比如复制粘贴一段精彩的网络文摘保存到
txt 文件中,比如在 Excel 中进行报表记录。
创建一个空文件:
import os
os.mknod("test.txt")
打开一个文件:
file = open('test.txt')
关于 open()函数对文件的打开模式:
- w:以写方式打开
- a:以追加模式打开 (从 EOF 开始, 必要时创建新文件)
- r+:以读写模式打开
- w+:以读写模式打开
- a+:以读写模式打开
- rb:以二进制读模式打开
- wb:以二进制写模式打开
- ab:以二进制追加模式打开
- rb+:以二进制读写模式打开
- wb+:以二进制读写模式打开
- ab+:以二进制读写模式打开
读取文件内容
- file.read([size]):size 为读取的长度,以 byte 为单位
- file.readline([size]) :读一行,如果定义了 size,有可能返回的只是一行的一部分
- file.readlines([size]) :把文件每一行作为一个 list 的一个成员,并返回这个 list。其实它的内部是通过循环调用 readline()来实现的。如果提供 size 参数,表示读取内容的总长,也就是说可能只读到文件的一部分。
写入文件
- file.write(str) :把 str 写到文件中,write()并不会在 str 后加上一个换行符
- file.writelines(seq):把 seq 的内容全部写到文件中(多行一次性写入),既接受一个字符串,
- 也接受一个字符串序列。
关闭文件
file.close()
除了使用 close()方法对文件进行显示的关闭。我们还能够借助 Python 提供的资源访问控制功能
with…as 实现文件的打开和关闭:
with open('test.txt','w') as file:
data = file.read()
以上代码就使用了文件的打开、读取和关闭。
栗子
我们来爬取长汀二手房的信息,代码有点粗糙,后期优化。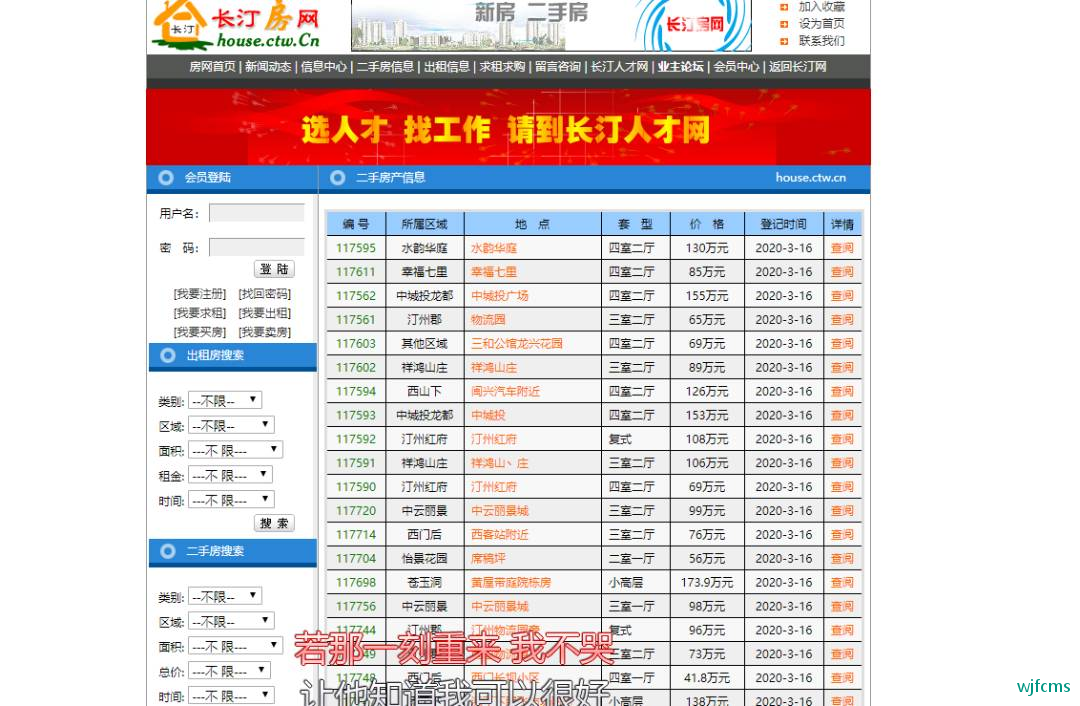
# coding:utf-8
# 引入相关模块
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "http://house.366300.com/houselist.asp?type=sale"
# 请求腾讯新闻的 URL,获取其 text 文本
wbdata = requests.get(url)
wbdata.encoding = 'gbk' # 将编码格式改为utf-8
# 对获取到的文本进行解析
soup = BeautifulSoup(wbdata.text, 'lxml')
# 从解析文件中通过 select 选择器定位指定的元素,返回一个列表
ids = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(1)>div>p>font>span")
areas = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(2)>div>span")
address = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(3)>div>span>a>font")
types = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(4)>div>span")
prices = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(5)>div>span")
times = soup.select(
"table.bk > tr> td:nth-child(2)> table:nth-child(4)>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td>table>tr>td:nth-child(6)>div>span")
dict = {}
for i in range(len(ids)):
if len(ids) > 30:
id_i = i + 1
else:
id_i = i
if len(areas) > 30:
area_i = i + 1
else:
area_i = i
if len(address) > 30:
addres_i = i + 1
else:
addres_i = i
if len(types) > 30:
type_i = i + 1
else:
type_i = i
if len(prices) > 30:
price_i = i + 1
else:
price_i = i
if len(times) > 30:
time_i = i + 1
else:
time_i = i
id = ids[id_i].get_text().strip()
area = areas[area_i].get_text().strip()
addres = address[addres_i].get_text().strip()
type = types[type_i].get_text().strip()
price = prices[price_i].get_text().strip()
time = times[time_i].get_text().strip()
data = {
'id': id,
'area': area,
'addres': addres,
'type': type,
'price': price,
'time': time,
}
dict[i] = []
dict[i].append(data)
with open('listings.txt', 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as files:
# 对返回的列表进行遍历
for n in dict:
str = '编号:' + dict[n][0]['id'] + ',' + '区域:' + dict[n][0]['area'] + ',' + '地点:' + dict[n][0][
'addres'] + ',' + '类型:' + dict[n][0]['type'] + ',' + '价格:' + dict[n][0]['price'] + ',' + '发布时间:' + dict[n][0]['time'] + '\n'
files.write(str)
结果: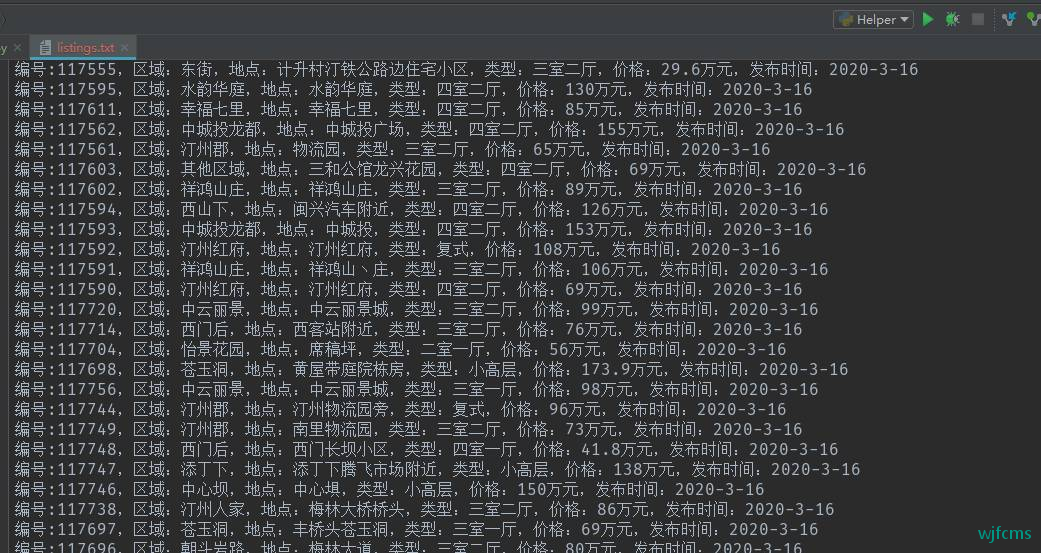





 微信收款码
微信收款码 支付宝收款码
支付宝收款码